Experiment Name: Study on Lathe Engine.
Theory:
A lathe is a machine that shapes
pieces of material. Usually the material being melded is wood or metal,
and is referred to as the "work." The most common lathes are woodworking
ones. The wood sits between two parts of the lathe called the headstock
and the tailstock. The two parts hold the work in place and spin it
quickly. When using wooden lathes the pieces are shaped by hand with a
chisel, while lathes that shape other materials, such as metal, have
chisels attached to an adjustable carriage that holds the cutting tools
in contact with the spinning metal. The carriage is controlled remotely
by the operator. Lathes can come in a variety of sizes. The smaller
bench top versions are usually affordable for the amateur and home
builder, while the heavy-duty, full-size models that are designed for
professionals are much more expensive. All of the lathes have a motor
that spins the wood through the headstock, the tool rest, and an
adjustable tailstock. Lathes differ in the length of material they can
hold, what materials they can cut, how powerful the motor is, the
diameter of the material that will fit, and the type of mechanism that
spins the work.
Objective:
1) To learn about different component of lathe engine.
2) To learn about its importance.
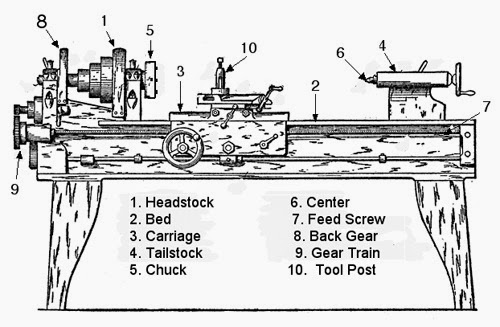
Component o lathe engine:
· Carriage.
· Head Stock
· Headstock Spindle
· Bed Saddle
· Apron
· Compound side rest.
· Back gear.
Parts of lathe machine:
Carriage :
The lathe carriage serves the purpose
of supporting, guiding and feeding the tool against the job during the
operation of the lathe. The carriage will present between head stock and
tail stock which will slides on the bed ways of the lathe bed. The
carriage will give feed to the tool and it holds the tool, for taper
turning the feed is cross feed, for turning it is longitudinal feed. The
carriage consists of the following parts.
1. saddle.
2. cross-slide.
3. compound Rest.
4. Tool post.
5. Apron.
Saddle: It is the part of the carriage which slides along the bed way and support the Cross-slide, compound rest and Tool post.
Cross-slide: The cross-slide
function is to provide cutting action to the tool and the action of
cutting tool will be perpendicular to centre line of lathe. It can
either be operated by hand, by means of the cross-feed screw, or may be
given power feed through the Apron Mechanism.
Compound Rest : The compound
Rest will be placed over the cross slide and it consists of a graduated
circular base which is having swivelling nature.
Tool post: It is the top most part of the carriage and is used for holding the tool or tool holder in position.
Apron: Apron houses the feed
mechanism, clutch mechanism split half nut, gears, leavers, The apron
wheel can be rotated by hand for longitudinal motion of the carriage.
Bed : The
bed of Lathe acts as the base on which the different fixed and
operations parts of the Lathe are mounted. Lathe beds are usually made
as single piece casting of semi-steel with the addition of small
quantity of steel scrap to the cast iron during melting; the material
‘cast iron’ facilitating an easy sliding action. In case of extremely
large machines, the bed may be in two or more pieces, bolted together to
from the desired length. Lathe Bed are heavy rigid structure which is
having high damping capacity for the vibrations generated by machines
during machining. The rigid structure will helps to avoid deflections.
The guides and ways which are present on the top of the bed will act as
rails and supports other parts like tail stock. The bed will be designed
in such a way that easily bolted to the floor of the machine shop.
Tail Stock:
It is also sometimes called the LOOSE
HEAD- STOCK or PUPPET HEAD. It is mounted on the bed of the lathe such
that it is capable of sliding along the latter maintaining its alignment
with the head stock. On common types of medium size or small size
lathes it is moved along the bed by hand, whereas in heavier types of
lathes it is moved by means of a hand wheel through a pinion which
meshes with the rack provided on the front of the lathe bed. The main
function of the Tail stock is to provide bearing and support to the job
which is being worked between centre. To enable this, the tail stock is
made to possess a number of parts which collectively help in its
successful function.
Head stock:
The head stock is the part of the lathe
which serves as a housing for the driving pulleys and back gears,
provides bearing for the machine spindle and keeps the latter in
alignment with the bed. It is a fixed part which will present on the
left side of the lathe bed. Head stock will consists of a hollow spindle
and drives unit like main spindle, feed reverse lever, live centre cone
pulley etc., The tapered bar with pointed or projected end is going to
grip the work piece between two centres of lathe bed.
Conclusion:>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>


No comments:
Post a Comment